
- #Github desktop clone archive#
- #Github desktop clone software#
- #Github desktop clone code#
- #Github desktop clone download#
- #Github desktop clone windows#
#Github desktop clone download#
Click the button (now labeled “Pull origin”) again to download those changes. If there are changes that need to be downloaded, you’ll see a small number by a downward pointing arrow. Click on the Fetch origin button at the upper right of the window. When you are editing files using GitHub desktop, it is important to have a disciplined work cycle to make sure that your work gets saved to the hub without merge conflicts.Īfter you’ve decided what branch you need to work on, it’s very important to make sure at the start that you are working on the most recent version of it by pulling any changes from Github. However, if you are working on more than one computer, or if you are working with a collaborator, it’s important to pull changes from GitHub each time you start working in order to avoid missing changes that were made on another computer or by a collaborator. If you are only working on one computer, the changes will generally only flow in one direction. Create commits after each stage in the work, then push the changes to GitHub.
#Github desktop clone code#
In this model, you just simply work as usual on your local computer using your preferred text or code editor.
#Github desktop clone archive#
The simplest way to use GitHub is simply as a way to archive the history of your own work on files in a project. To see the commit history of the newly cloned repository, from within the repository’s local directory, enter git log
#Github desktop clone windows#
Here’s how it looks on a Windows system:ĭuring the cloning process, the local repository is associated with the particulary GitHub repository that was cloned, which is referred to as origin. git directory and any files and directories that were in the cloned repository (in this example, only the README.md document). In the example above: git clone Īs a result, the subdirectory will be created along with the hidden.
Type git clone followed by the URL you copied, then press Enter. In the console, navigate to the directory that you want to be the parent directory of the directory for the local repository. The comparable procedure on the command line requires acquiring the URL to the GitHub repository.Īfter clicking the Clone or download button, copy the URL by clicking on the clipboard icon. More on this in the next lesson…Ĭommand line comparison Remember that you can skip this section if you don’t care about the command line. The second column (“Current Branch”) will normally be set at “master” unless you have created another branch.

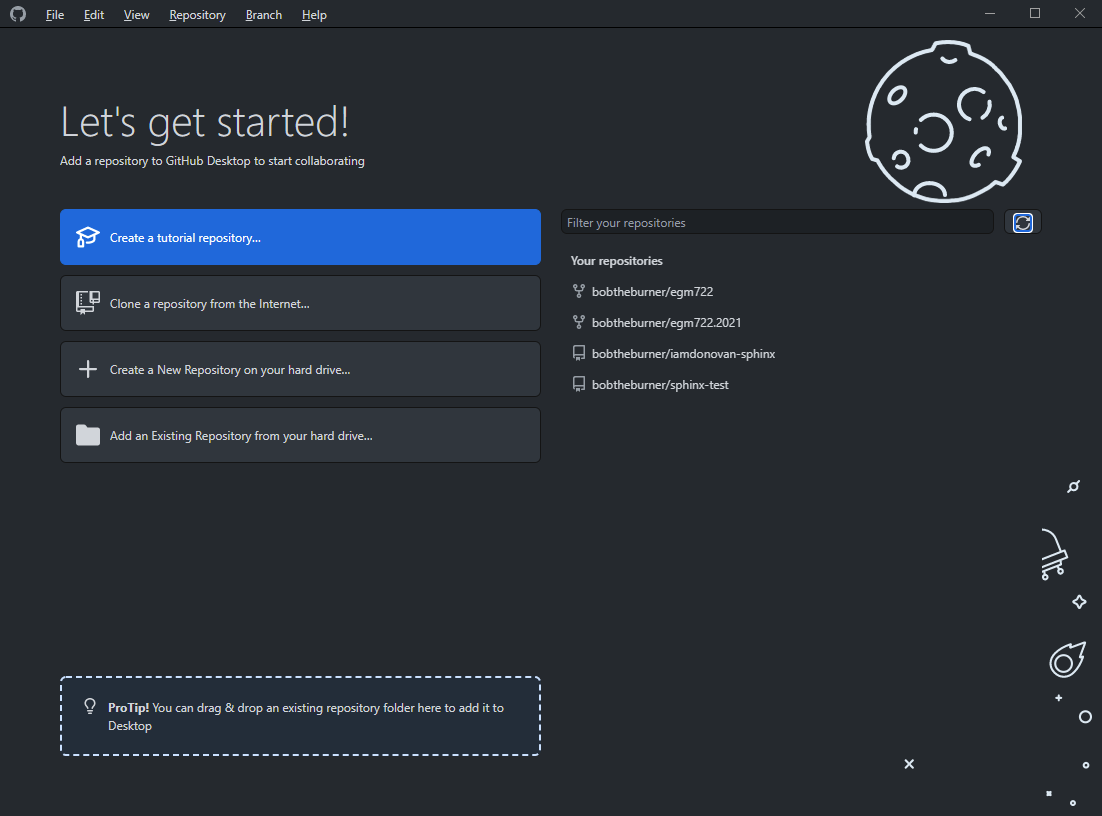
Once you’ve selected a location, the desktop client will default to that location the next time you clone.Īfter you’ve finished the cloning process, in the left column of the client, you’ll see either changed files or the commit history, depending on which tab you’ve selected. Click on the name of the repo you want to clone and you’ll have an opportunity to select the directory where you want the local copy of the repo to live on your computer. Repos that are forks you’ve made of some other user’s repo will have a little “fork” symbol. Repos that you own or to which you have write access will show up with little book icons. You’ll be presented with a list of repositories at to which you have access. Click on the Add dropdown and select “Clone Repository…”. The process described here will work for cloning one of your own repositories, a repository that you’ve forked to your account from elsewhere, or another repository that you don’t own, but to which you have been given write access.ĭrop down the Current Repository menu in the upper left of the window.

You can also initiate the cloning process from your local computer from within the GitHub Desktop application.
#Github desktop clone software#
If you choose Open in Desktop, the repository will open in the GitHub Desktop software after it downloads. You can initiate cloning of a repository from the website by clicking on the Clone or download button in the upper right of the repo page on the GitHub website. Cloning a GitHub Repository to Your Local Computer You can only have one copy checked out at a time. When you check out one branch, you obtain a copy of it and you stop using another copy. Since your local copy of the repository contains every branch in the repository, how do you determine which branch you will actually be working with on your hard drive? In Git, the process of switching branches is called “checking out” a branch. That includes all of the branches in the repository and all of the commit histories of every branch.

The cloning process involves creating a complete copy of a repository on your local computer. GitHub desktop is available for every major operating system at. Previous page: Introduction to GitHub The GitHub desktop clientĪlthough every Git operation can be carried out using the command line, many users prefer to use GitHub Desktop, a graphical interface for interacting with GitHub.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
